1. 새 프로젝트 생성
프로젝트명 tenco_swing
tenco_swing.ch01 패키지 안에 새로운 클래스 생성
클래스명 FlowLayoutEx
--- 기본적으로 세팅 해주고 시작할 코드형식 ---
package swing;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class FlowLayoutEx extends JFrame {
// 생성자
public FlowLayoutEx() {
super.setTitle("FlowLayout 연습");
super.setSize(500, 500);
super.setVisible(true);
super.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// 생성자에서 메서드 호출 가능
initData();
setInitLayout();
}
// 멤버 변수를 초기화 하는 기능
public void initData() {
}
// 컴포넌트들을 배치하는 기능
public void setInitLayout() {
}
}
위 사진 처럼 세팅해주지 않으면 JFrame 상속했을 때 오류남
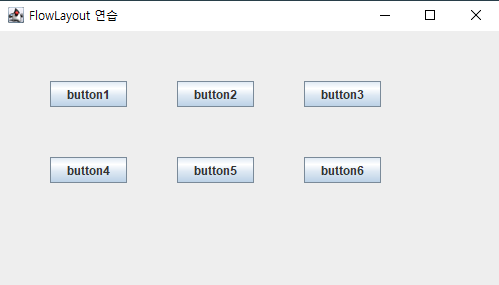
2. 배치 관리자 FlowLayout
버튼 6개 만들어서 띄워보기
package ch01;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
// Swing -> 배치 관리자 : FlowLayout
// 컴포넌트들을 (버튼, 라벨) 등을 수평, 수직으로 배치를 해주는 클래스이다.
public class FlowLayoutEx extends JFrame {
private JButton button1;
private JButton button2;
private JButton button3;
private JButton button4;
private JButton button5;
private JButton button6;
// 생성자
public FlowLayoutEx() {
super.setTitle("FlowLayout 연습");
super.setSize(500, 500);
super.setVisible(true);
super.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// 생성자에서 메서드 호출 가능
initData();
setInitLayout();
}
// 멤버 변수를 초기화 하는 기능(값 넣다)
public void initData() {
button1 = new JButton("button1");
button2 = new JButton("button2");
button3 = new JButton("button3");
button4 = new JButton("button4");
button5 = new JButton("button5");
button6 = new JButton("button6");
}
// 컴포넌트들을 배치하는 기능
public void setInitLayout() {
// 배치 관리자 --> BorderLayout 이라는 배치관리자가 기본으로 활용된다.
// FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout();
// setLayout(flowLayout);
// 배치관리자 생성 및 JFrame 셋팅
super.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEADING, 50, 50)); // 배치관리자 --> FlowLayout
// 컴포넌트들을 붙이다.
super.add(button1);
super.add(button2);
super.add(button3);
super.add(button4);
super.add(button5);
super.add(button6);
}
// 코드 테스트
public static void main(String[] args) {
// FlowLayoutEx f1 = new FlowLayoutEx(); <----- 부를 수 있는 이름이 있는 상태
new FlowLayoutEx(); // <----- 익명 클래스
// 다시 접근해서 사용할 일 없으면 생성만 해도됨.
} // end of main
}
습관 들이기
ctrl + T 로 상속관계를 모두 확인
ctrl + 좌클릭 으로 원시코드 확인
매개변수로 어떤 타입을 넣어줘야 하는지, 다형성을 이용해서 어떤 타입으로도 쓸 수 있는지 알 수 있고
미리 설정된 상수 값을 볼 수 있음
코드 리팩토링 - 배열과 반복문을 활용해서 코드를 수정하시오.
package ch01;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class FlowLayoutEx2 extends JFrame {
// 배열 활용
private JButton[] buttons;
// 생성자
public FlowLayoutEx2() {
super.setTitle("FlowLayout 연습");
super.setSize(500, 500);
super.setVisible(true);
super.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// 생성자에서 메서드 호출 가능
initData();
setInitLayout();
}
// 멤버 변수를 초기화 하는 기능(값 넣다)
public void initData() {
buttons = new JButton[6];
// 반복문 활용
for (int i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
buttons[i] = new JButton("button" + (i + 1));
}
}
// 컴포넌트들을 배치하는 기능
public void setInitLayout() {
// 배치관리자 생성 및 JFrame 셋팅
super.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEADING, 50, 50)); // 배치관리자 --> FlowLayout
// 컴포넌트들을 붙이다.
// 반복문 활용
for (int i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
super.add(buttons[i]);
}
}
// 코드 테스트
public static void main(String[] args) {
new FlowLayoutEx2(); // <----- 익명 클래스
} // end of main
}3. 배치 관리자 BorderLayout
package ch01;
// ctrl shift O 는 안쓰는 import 삭제
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class BorderLayoutEx1 extends JFrame{
// 생성자
public BorderLayoutEx1() {
initData();
setInitLayout();
}
public void initData() {
setTitle("borderLayout 연습");
setSize(600, 600);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public void setInitLayout() {
// 배치 관리자 선정 (컨테이너)
// BorderLayout -- 컴포넌트들을 동서남북가운데로 배치 시켜주는 레이아웃이다.
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add(new JButton("동"), BorderLayout.EAST);
add(new JButton("서"), BorderLayout.WEST);
add(new JButton("남"), BorderLayout.SOUTH);
add(new JButton("북"), BorderLayout.NORTH);
add(new JButton("센터"), BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new BorderLayoutEx1();
}
}코드 리팩토링 - 배열과 반복문을 활용해서 코드를 수정하시오.
package ch01;
// ctrl shift O 는 안쓰는 import 삭제
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class BorderLayoutEx2 extends JFrame{
final int WIDTH = 600;
final int HEIGHT = 600;
JButton[] buttons;
String[] directions = {BorderLayout.EAST, BorderLayout.WEST, BorderLayout.SOUTH, BorderLayout.NORTH, BorderLayout.CENTER};
// 생성자
public BorderLayoutEx2() {
initData();
setInitLayout();
}
public void initData() {
setTitle("borderLayout 연습");
setSize(WIDTH, HEIGHT);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
buttons = new JButton[directions.length];
}
public void setInitLayout() {
// 배치 관리자 선정 (컨테이너)
// BorderLayout -- 컴포넌트들을 동서남북가운데로 배치 시켜주는 레이아웃이다.
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
// 반복문을 활용해서 코드를 완성
for (int i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
add(new JButton(directions[i]), directions[i]);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new BorderLayoutEx2();
}
}'Java > Swing 프로젝트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Swing Key Listener - 6 (0) | 2024.04.30 |
|---|---|
| Swing 이벤트 리스너 - 5 (0) | 2024.04.29 |
| Swing image 위에 image - 4 (0) | 2024.04.29 |
| Swing image 출력 - 3 (0) | 2024.04.29 |
| Swing 기초연습 - 2 (0) | 2024.04.26 |



