목차
큐(Queue) 구현하기
💡 학습 목표
1. Queue 에 대한 개념을 알아 보자.
2. 배열을 활용한 큐(Queue) 구현하기
3. 배열을 활용한 큐를 순환 구조로 수정해 보기
1. Queue 에 대한 개념을 알아 보자.
- 큐 (Queue)는 데이터를 저장하는 선형 자료구조로, 차례를 기다리는 줄이라는 의미를 가지고 있는 단어처럼 먼저 들어온 자료부터 순서대로 처리하는 방식을 말한다.
- 한 쪽 끝에서는 자료의 삽입 연산만 가능하고 반대쪽 끝에서는 삭제만 가능한 구조로서 선입선출(FIFO : First In First Out)의 특징을 가진다.
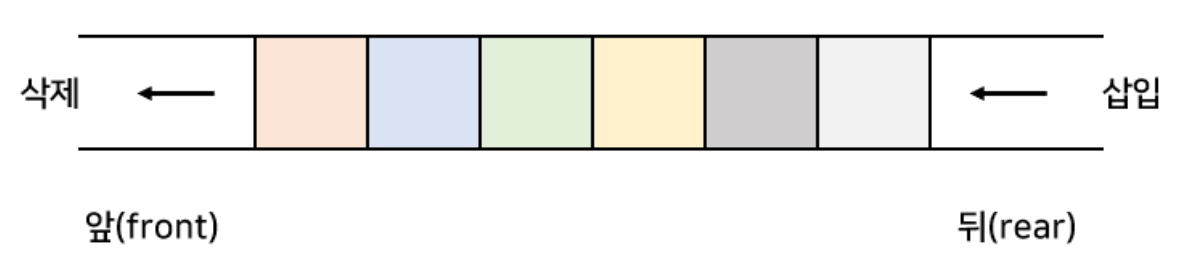
Queue의 특징
- 맨 앞(front) 에서 자료를 꺼내거나 삭제하고, 맨 뒤(rear)에서 자료를 추가 함
- Fist In First Out (선입선출) 구조
- 일상 생활에서 일렬로 줄 서 있는 모양
- 순차적으로 입력된 자료를 순서대로 처리하는데 많이 사용 되는 자료구조
- 콜센터에 들어온 문의 전화, 메세지 큐 등에 활용됨
- jdk 클래스 : ArrayList
2. 배열을 활용한 큐(Queue) 구현하기
시나리오 코드 1
package structure.ch03;
public class IntArrayQueue {
private int[] array;
private int front; // 큐의 시작점
private int rear; // 큐의 끝 지점
private int capacity; // 큐의 용량
private int size; // 요소의 개수
private final int ERROR_NUM = -9999;
public IntArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
array = new int[this.capacity];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = -1;
this.size = 0;
}
// 편의 기능 만들어 보기
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
// todo - 1 데이터 넣기 기능 구현
public void enqueue(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("큐 메모리 공간이 가득");
} else {
// rear : -1 시작
array[++rear] = item;
size++;
}
}
// todo - 2 데이터 꺼내기
public int dequeue() {
int item = ERROR_NUM;
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("큐 메모리 공간에 요소가 없음");
} else {
// 잠시 데이터 꺼내보기
item = array[front]; // 0번째 요소에 접근
for(int i = front; i < rear; i++) {
array[i] = array[i+1];
}
// 마지막 요소를 초기화 처리한다
array[rear--] = 0;
size--;
}
return item;
}
// todo - 3 데이터 찾기 (peek)
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("큐 메모리 공간에 요소가 없음");
return ERROR_NUM;
} else {
return array[front];
}
}
// 코드 테스트
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntArrayQueue queue = new IntArrayQueue(3);
// 데이터 넣기
queue.enqueue(100);
queue.enqueue(200);
queue.enqueue(300);
queue.enqueue(400); // 안들어감
// 데이터 꺼내고 삭제 처리
// queue.dequeue(); // 맨 처음 들어온 녀석부터 꺼내지고 삭제처리 된다.
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
queue.enqueue(100);
queue.enqueue(200);
queue.enqueue(300);
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println(queue.peek());
} // end of main
}이 방식은 배열의 끝에 도달했을 때 자동으로 시작 위치로 돌아가지 않으므로 순환 구조가 아닌 일반 큐의 동작 방식
3. 배열을 활용한 큐를 순환 구조로 수정해 보기
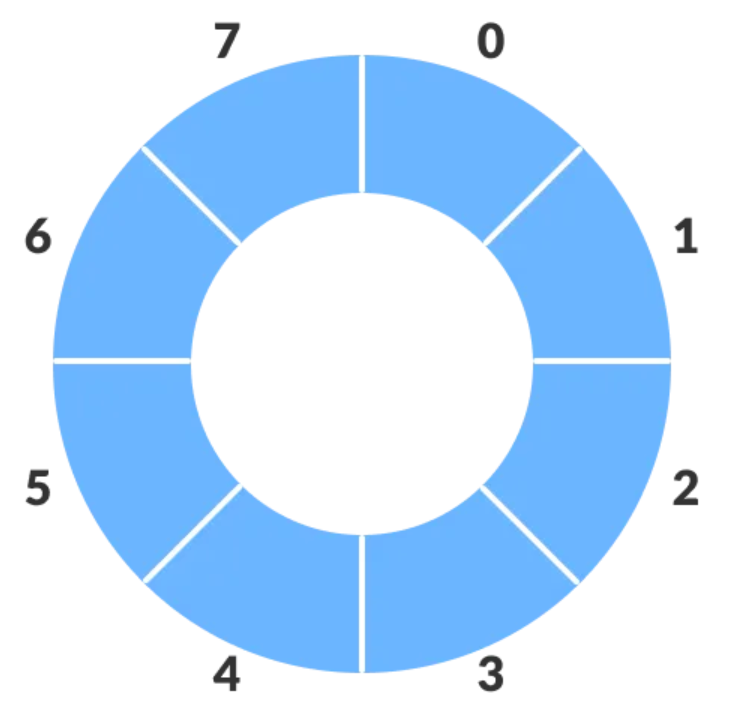
시나리오 코드 2
enqueue, dequeue 메서드 수정
package structure.ch03;
public class IntArrayQueue2 {
private int[] array;
private int front; // 큐의 시작점
private int rear; // 큐의 끝 지점
private int capacity; // 큐의 용량
private int size; // 요소의 개수
private final int ERROR_NUM = -9999;
public IntArrayQueue2(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
array = new int[this.capacity];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = -1;
this.size = 0;
}
// 편의 기능 만들어 보기
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
// todo - 1 데이터 넣기 기능 구현
public void enqueue(int item) {
// 코드 수정
// [10][20][30]
// 나머지 연산자를 활용 한다 (순환구조)
// 1 = 1 % 5; 몫 0, 나머지 1
// 2 = 2 % 5; 몫 0, 나머지 2
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
array[rear] = item;
size++;
if (size >= capacity) {
size = capacity;
}
}
// todo - 2 데이터 꺼내기
public int dequeue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
return ERROR_NUM;
}
int item = array[front];
// [10] [20] [30]
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
size--;
return item;
}
public void printAll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 코드 테스트
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntArrayQueue2 queue = new IntArrayQueue2(3);
// 데이터 넣기
queue.enqueue(100);
queue.enqueue(200);
queue.enqueue(300);
queue.enqueue(400);
queue.enqueue(500);
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
// queue.printAll();
} // end of main
}
'Java > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컬렉션 프레임 워크 - 6 (0) | 2024.05.09 |
|---|---|
| LinkedList 구현해보기 - 5 (0) | 2024.05.08 |
| 배열을 활용한 Stack 구현해보기 - 3 (0) | 2024.05.03 |
| 자료구조 개론 - 1 (0) | 2024.05.02 |
| Java 배열을 활용한 객체 만들기 - 2 (0) | 2024.05.02 |


